Next.js is a React framework for building full-stack web applications. Here’s how I leveraged it to create my portfolio.
Why Choose Next.js?
I'm using Next.js 13+ with the App Router, and I chose it strategically based on my business and technical goals:
Straightforward routing and support for complex UI layouts
Easy integration with headless CMS platforms
Fast rendering and great performance out of the box
Strong built-in SEO and accessibility features
How the Project Is Organized
This project is structured using the App Router paradigm.
1 — File Structure & Routing
The project includes five (5) main routes and a single shared UI wrapper (layout.tsx). Screenshot: Folder structure
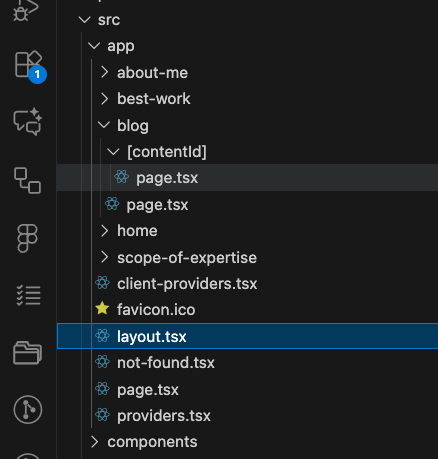
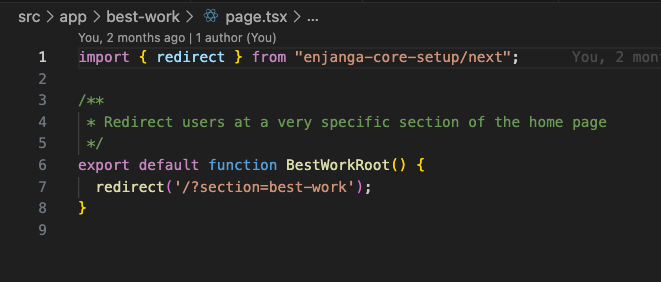
Three (3) of these routes are actually rendered within the home page because their content isn’t substantial enough to justify separate pages. Navigating to these routes redirects users to the homepage (if they aren’t already there) and automatically scrolls to the correct section.
2 — Rendering Mode
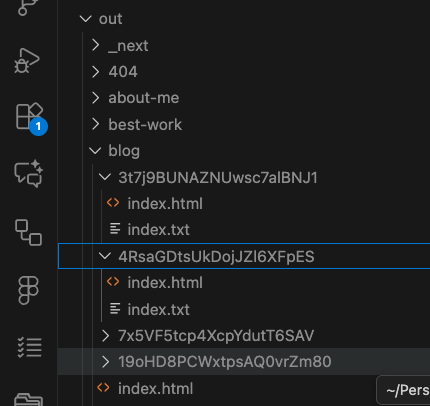
The entire application uses Static Site Generation (SSG).
With SSG, data is fetched from Contentful during the build step, and the output is a set of pre-generated HTML files. There is no need for real-time data fetching or frequent content refreshes, making SSG ideal for my portfolio.
Since this project doesn’t require dynamic data, frequent updates, or client-side state changes, SSG provides the fastest and most efficient rendering strategy.
3 — Server vs. Client Components
I keep components server-based whenever possible. Server components handle:
API data fetching
Metadata configuration
SEO-critical structure
High-performance rendering
Client components are used only when required, such as when using browser APIs, interactive UI elements, or React hooks that depend on the DOM.
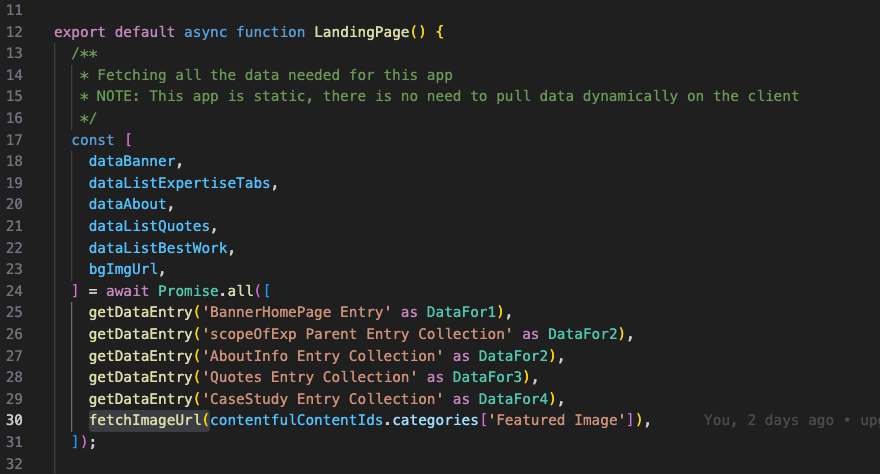
4 — Data Fetching
All API requests are performed server-side. Content is fetched from Contentful as early as possible, then passed down through:
Props (for route-level components)
Context providers (for deeper component hierarchies)
This keeps data fetching centralized, predictable, and optimized for SSG.
Optimization and Caching
Next.js includes several built-in caching and optimization layers that perfectly complement SSG:
Build-Time Caching: Pre-rendered pages are cached at the CDN edge.
Request-Level Caching: fetch() calls are automatically cached.
Full Route Caching: With the App Router, pages are static by default unless explicitly configured otherwise.
These optimizations significantly reduce load time and server overhead.
Takeaways and Next Steps
Next.js has allowed me to build a fast, scalable, and highly efficient platform tailored to my business needs. The folder-based routing system, server-side rendering approach, and predictable data-fetching architecture made for a powerful and maintainable setup.
Next steps
For future projects, I’d like to explore:
Additional rendering strategies (ISR, CSR)
API Routes (not available in strict SSG workflows)
Authentication/authorization frameworks (OAuth, etc.)
Stateless token systems (JWT)
Global state management libraries like Zustand
…and many more advanced features